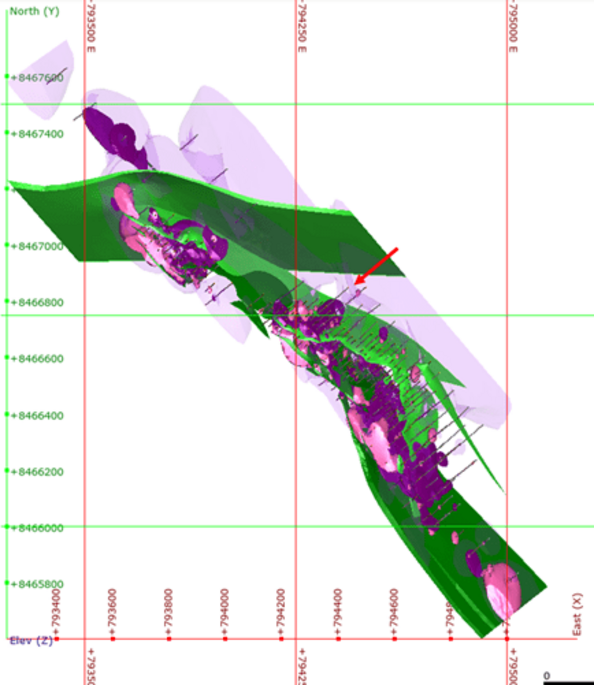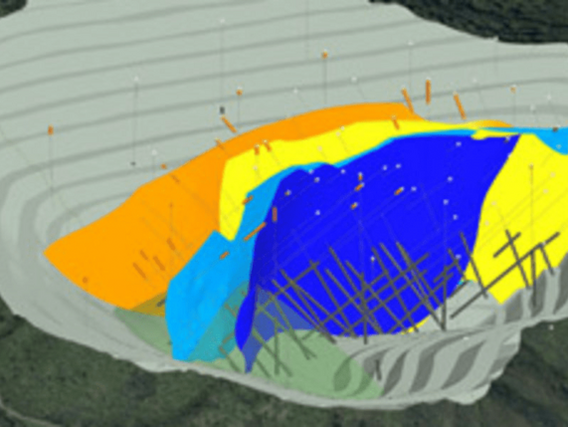
Geological modelling is the process of converting and reconstructing geology and its processes into a 3D computer model. The model includes structural, lithological, geochemical and geophysical data, geophysical channel data, trench data, borehole data and other sampling data are included in the model sampling data.
In other words, all available data is integrated into a three-dimensional model of the geology - on and below the surface. Detailed knowledge of a mineral reserve is the key to assessing the economics of mining ventures.
Mine Planning is the process of determining the most efficient methodologies and activities for mining and extraction, with a view to making the best use of mineral resources.
Do you know the relationship between the two concepts?