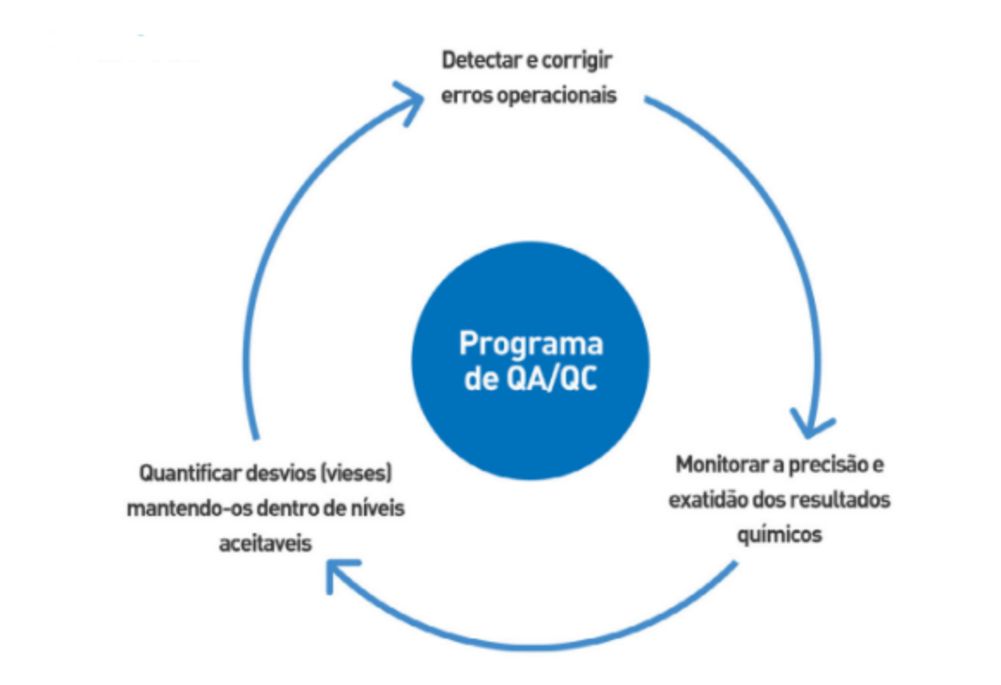
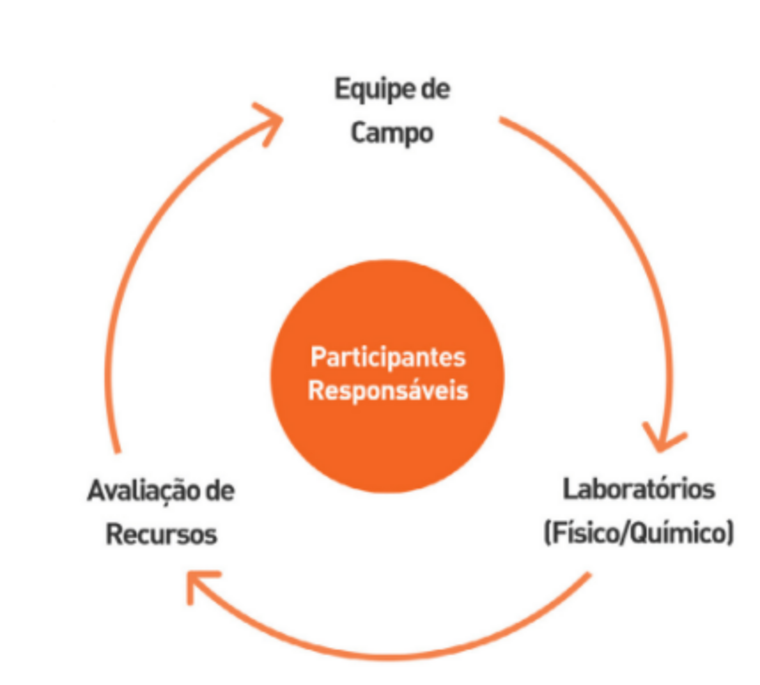
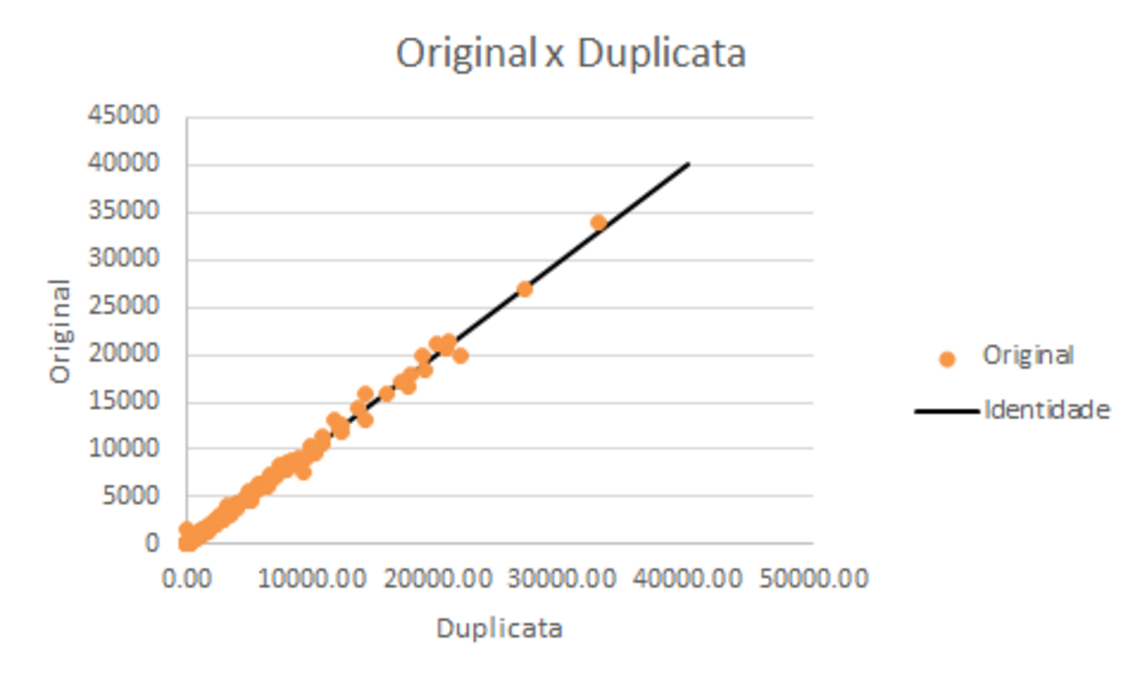
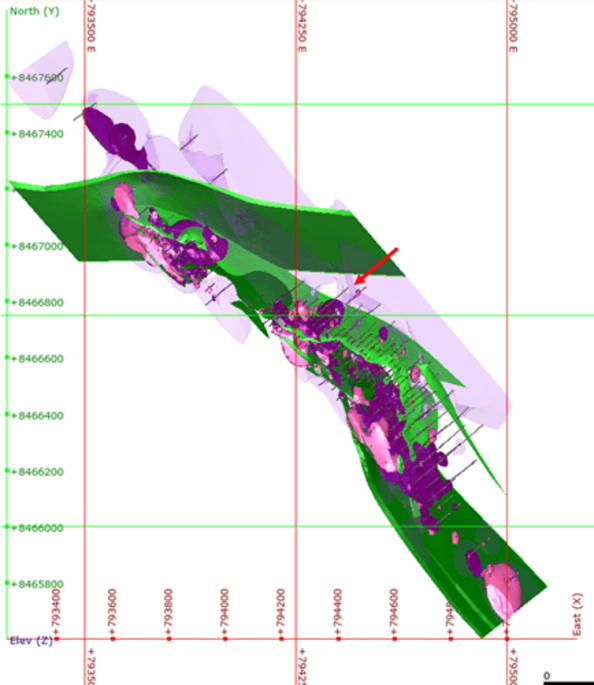
One of the main objectives of mining is to make the ore exploited marketable. For this to be possible, strict quality control is required at all stages of the process (exploration, prospecting and mineral research).
However, the use of good practices was not widely demanded in mining projects until the 1990s. The application of standards and procedures to achieve data reliability was demanded after the Bre-X project scandal. Bre-X project scandal in 1997.
The Bre-X affair is considered the biggest fraud in mining history. This event cast great doubt on the credibility of resource and reserve classifications and was the starting point for the consolidation of international behaviour.